








Scanning through photos recently, I stumbled upon this image, taken in a Boston Pizzeria…
Indeed, grace.
Yesterday’s service could not have been more delightful, beginning with a baptism and culminating with a rousing rendition of “Amazing Grace“.

The relationship of many western consumers to the internet giants is much like that which Václav Havel described for citizens living under the Soviet empire
The business model of the internet,” writes the security expert Bruce Schneier in his excellent new book Data and Goliath, “is surveillance.” States engage in it for their own inscrutable purposes and – as we know from Edward Snowden – they do it on a colossal scale. But the giant internet companies do it too, on an equally large scale. The only difference is that they claim that they do it with our consent, whereas the state doesn’t really bother with that.
A big mystery for those of us who worry about the long-term implications of surveillance is why internet users seem generally to be unconcerned about this. It varies from culture to culture, of course: the citizens of Germany are more perturbed about it than are the British; but that’s understandable because large numbers of Germans had the experience of living under the analogue surveillance run by the Stasi. And in the US, endemic suspicion of the federal government keeps some people awake at night. But on the whole, across the world, internet users seem relatively unfazed by what’s going on.
Walt saw beyond what people were used to. They were used to the short cartoon.
It’s interesting how people cannot see beyond what they’re used to.
There’s a famous statement by Henry Ford that before the Model T if you asked people what they wanted, they would say, “A faster horse.”
My own partner at Pixar for 25 years, Steve Jobs, never liked market research. Never did market research for anything.
Skyr, realized Ásmundsson, was nutritious, wholesome, and a formidable alternative to the “sugary crap” pervading the American culinary landscape. So, like any self-sufficient Icelander, he set out to make it for his son.
To learn the ropes, he journeyed to the eastern Iceland town of Egilsstaðir and shadowed an 82-year-old dairyman. The skyr maker offered simple advice: “Get the best milk. Skim the fat. Add live cultures. Let it set. Strain the liquid. When it looks really thick, strain even more.”
In May 2011, with little real-world business experience, and nothing more than a traditional recipe for skyr, Ásmundsson decided to start a yogurt company.
Wikipedia on the New Church. The new church houses the Stalingrad Madonna.
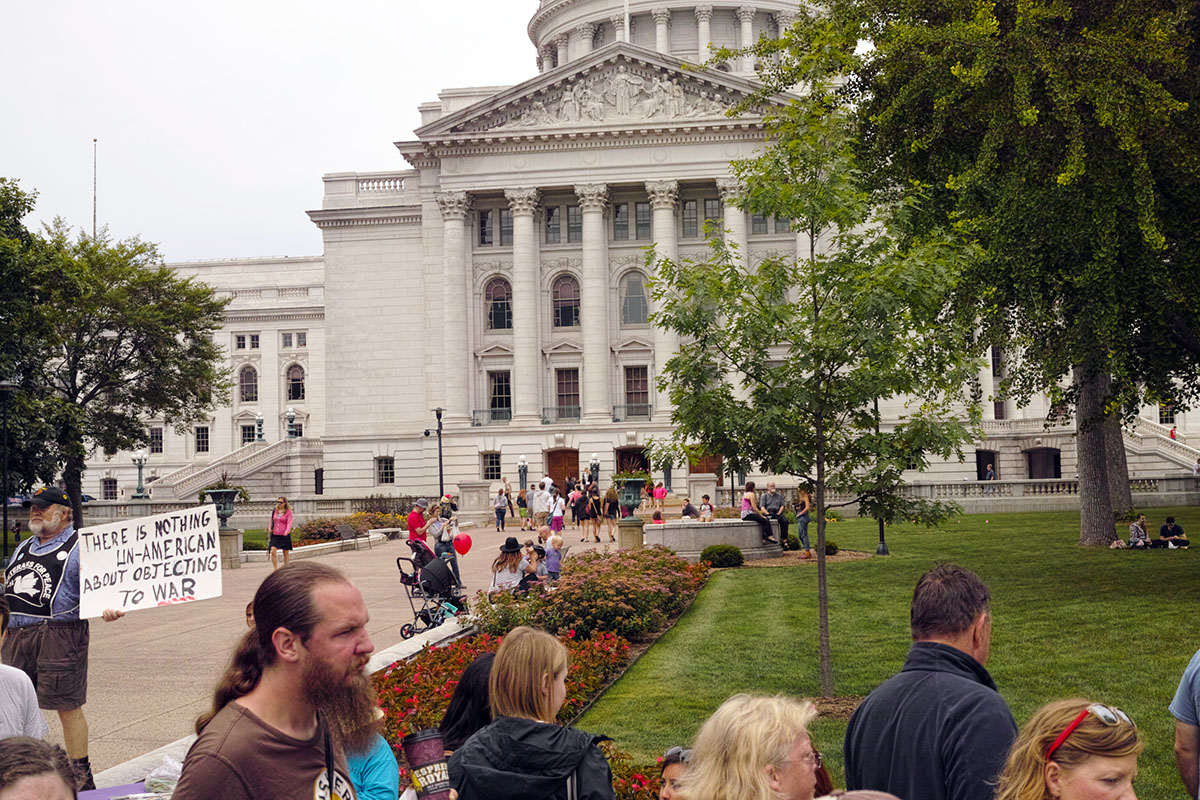
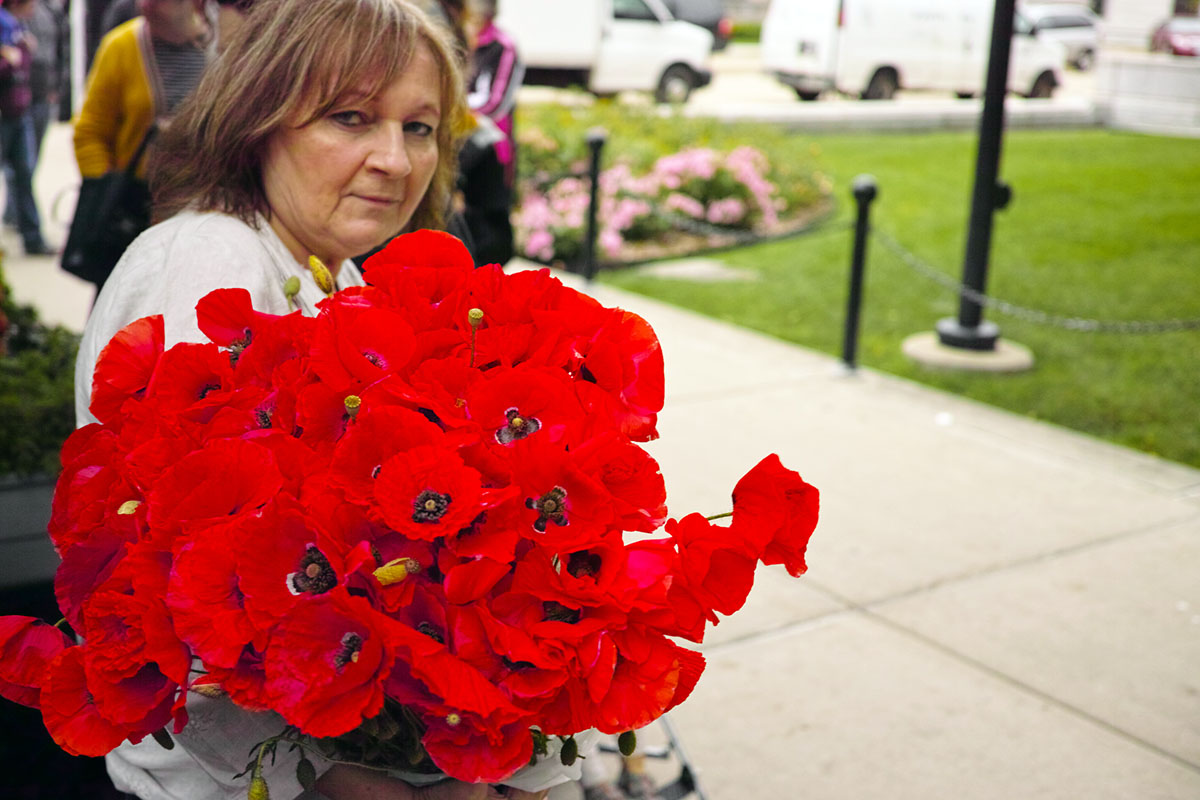
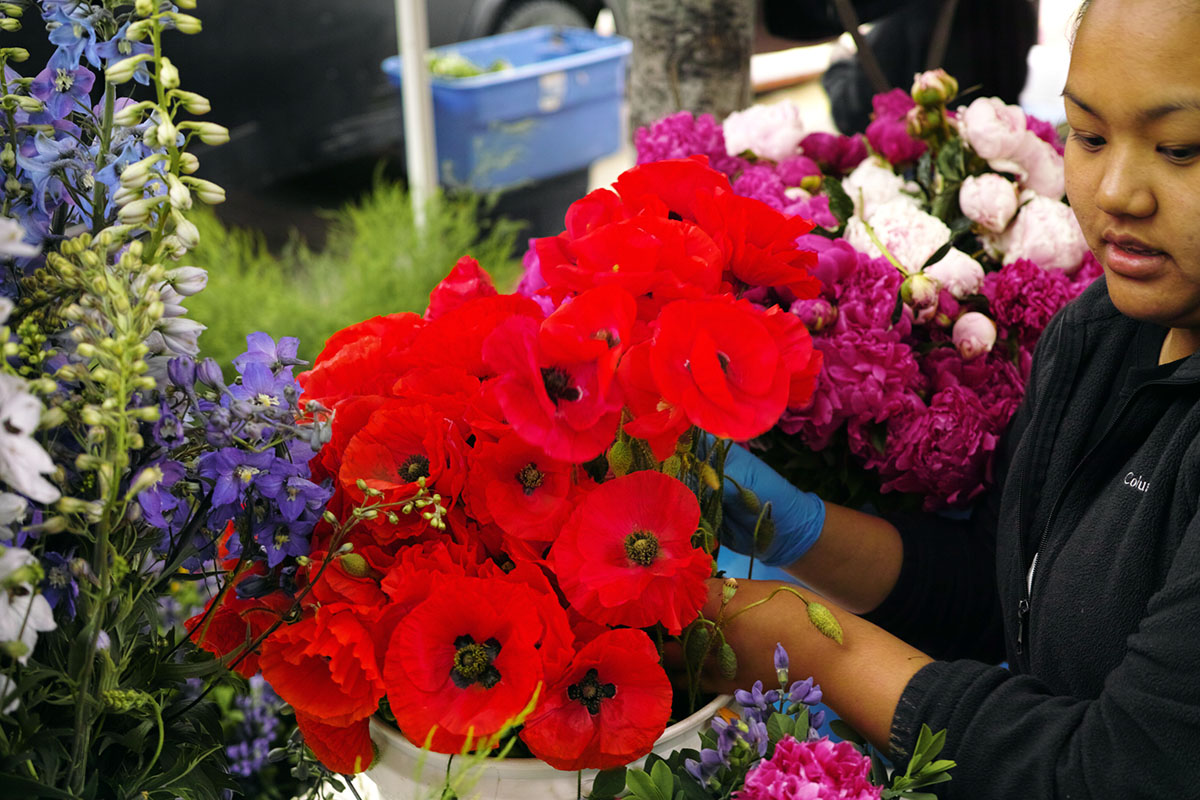
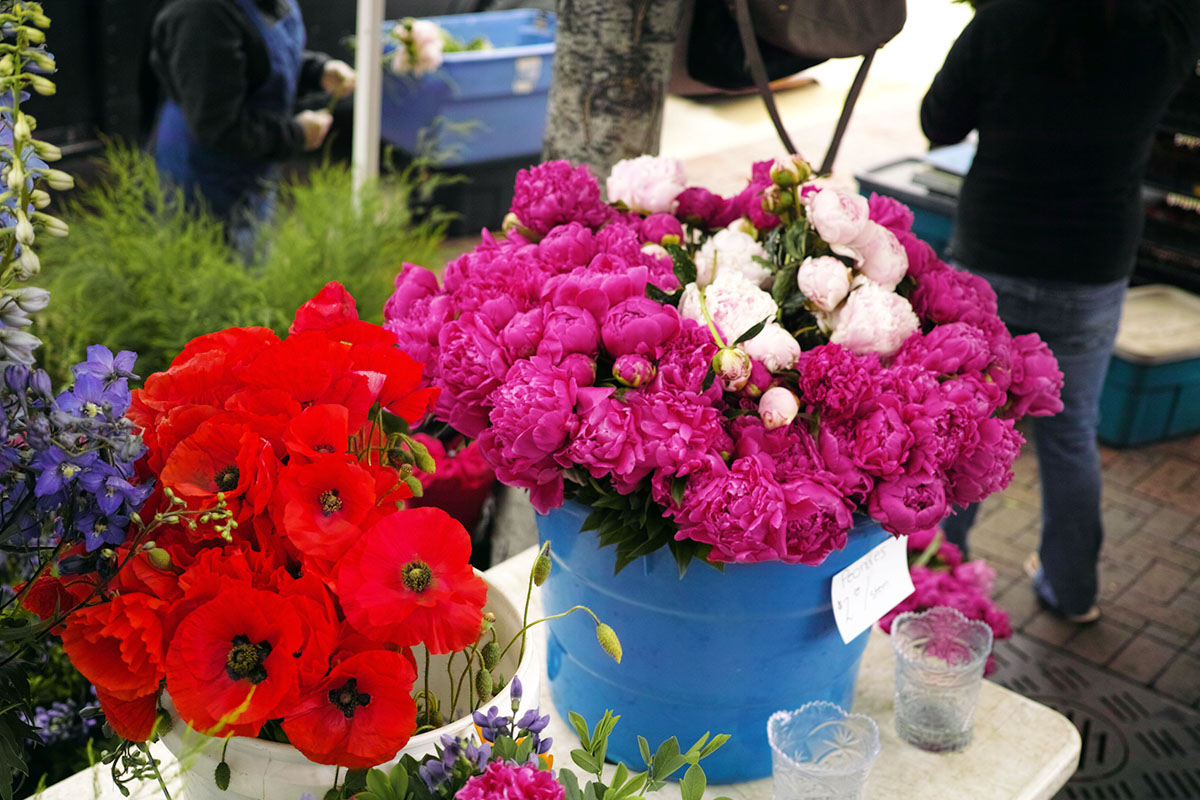
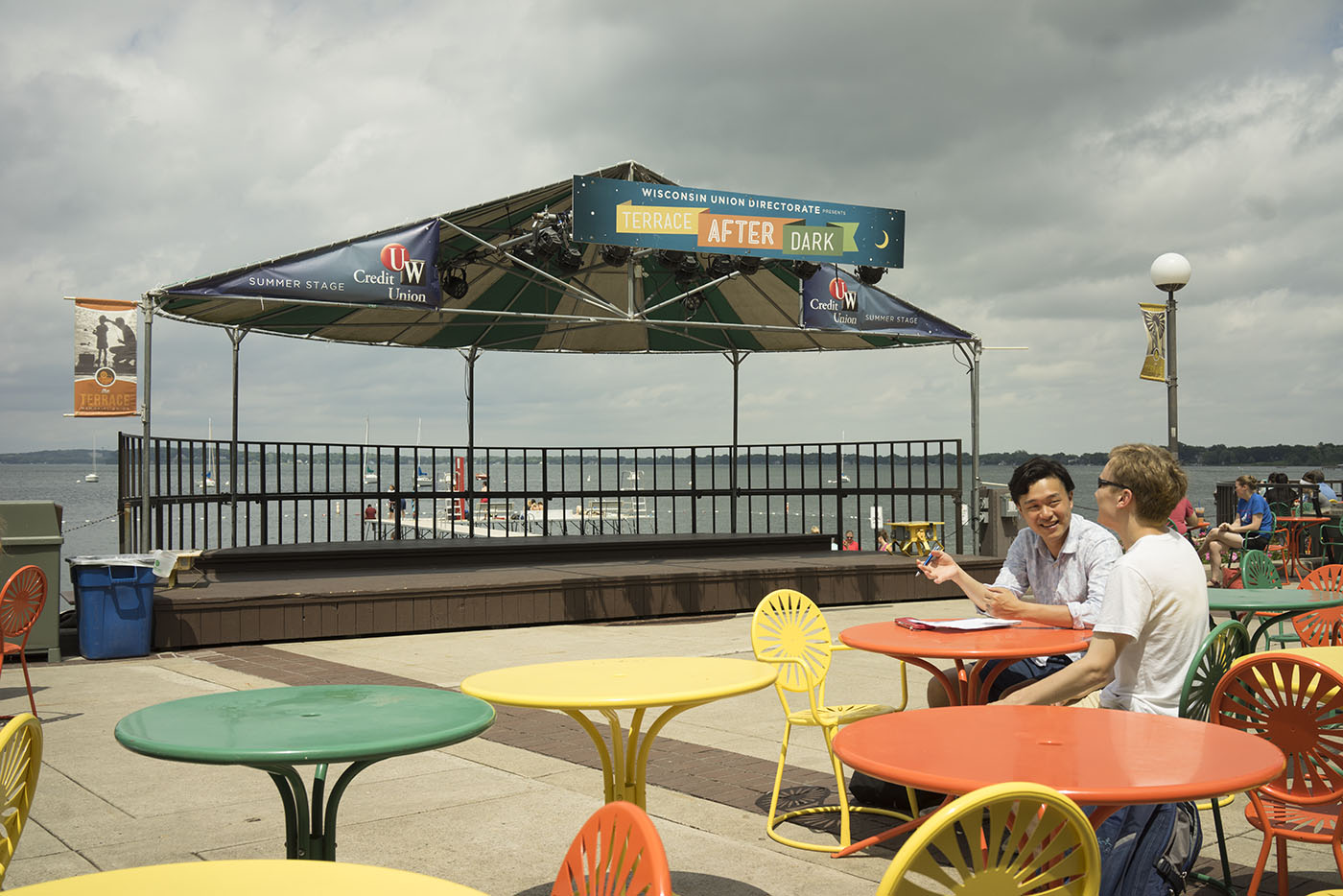






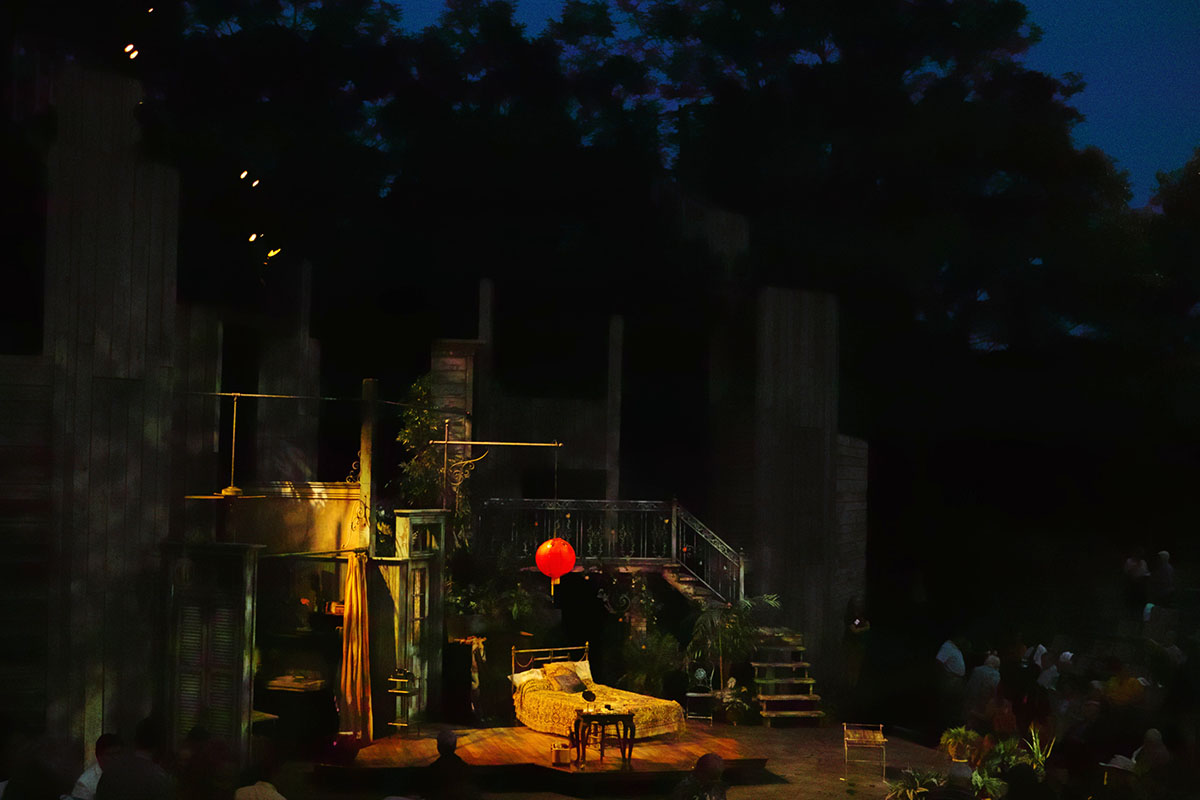


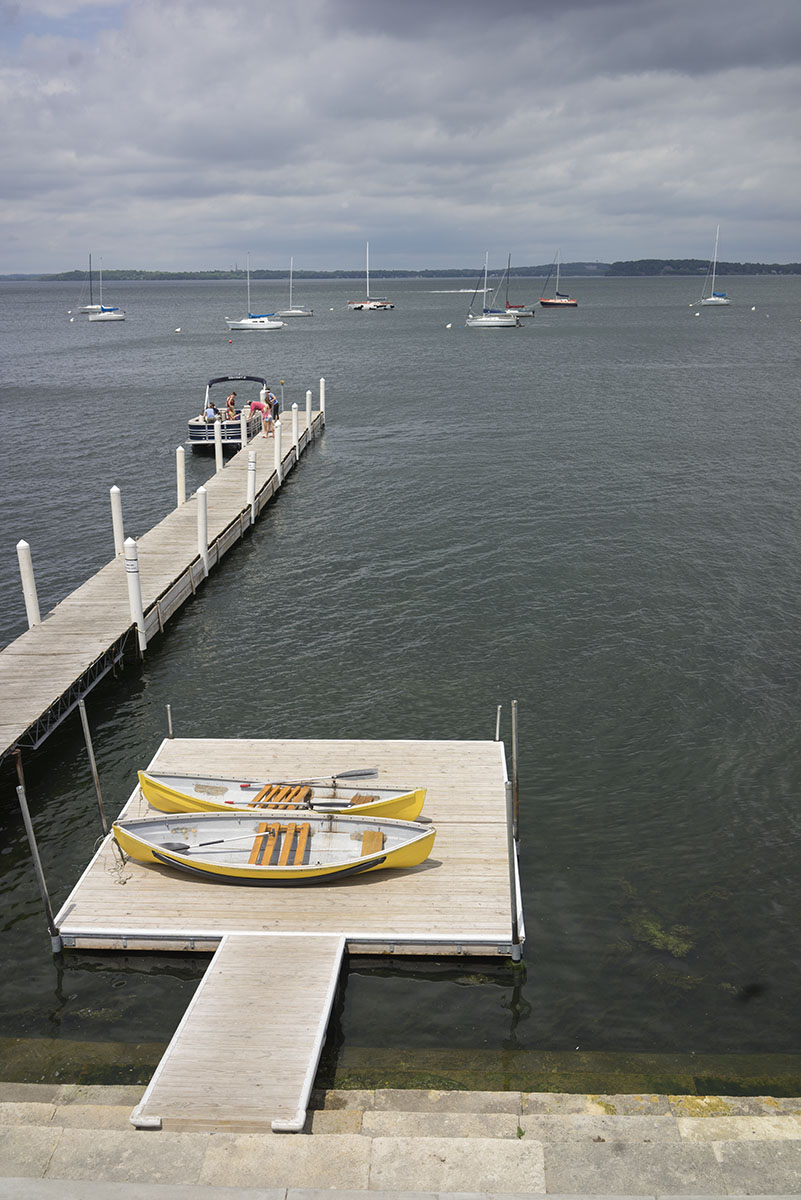

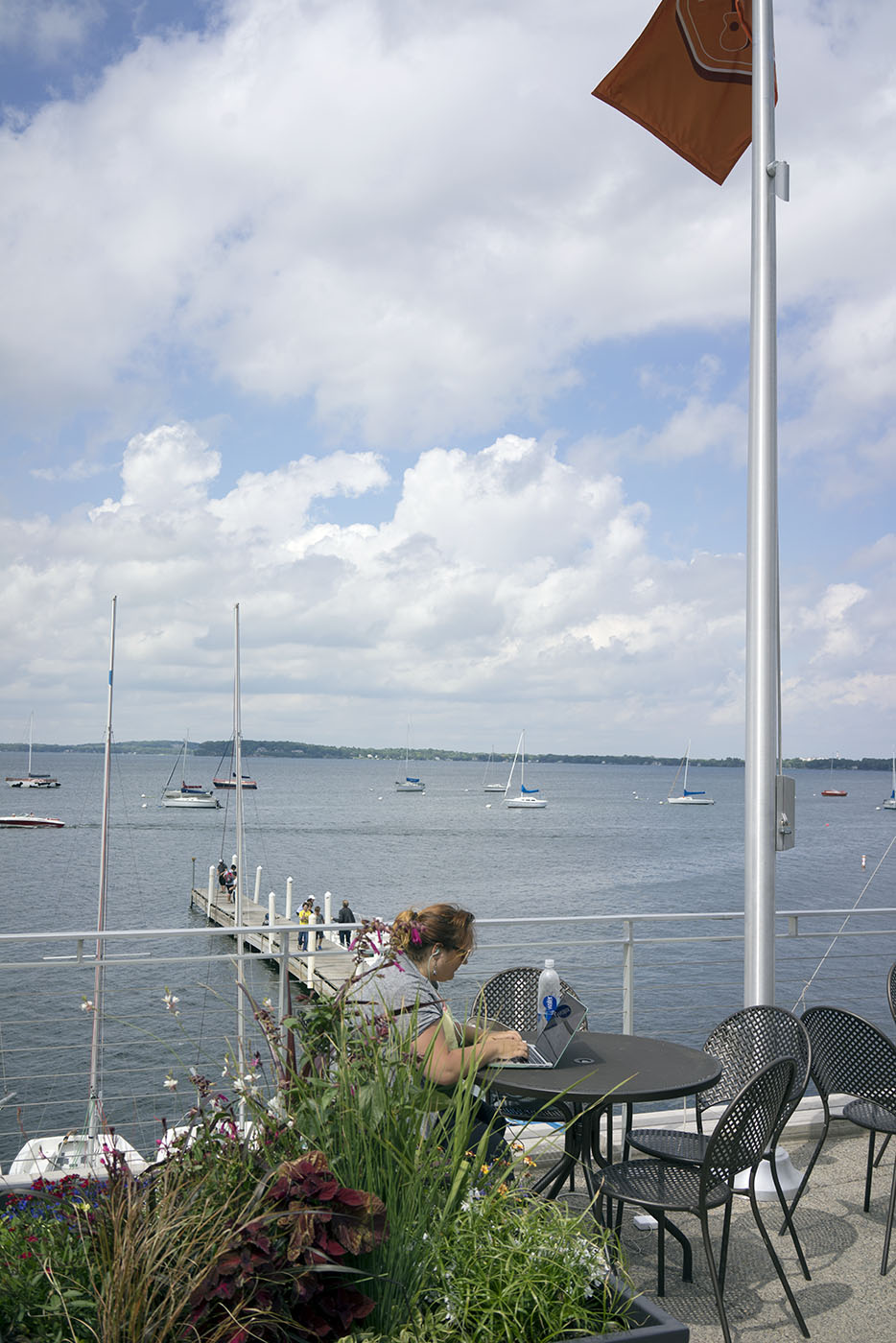


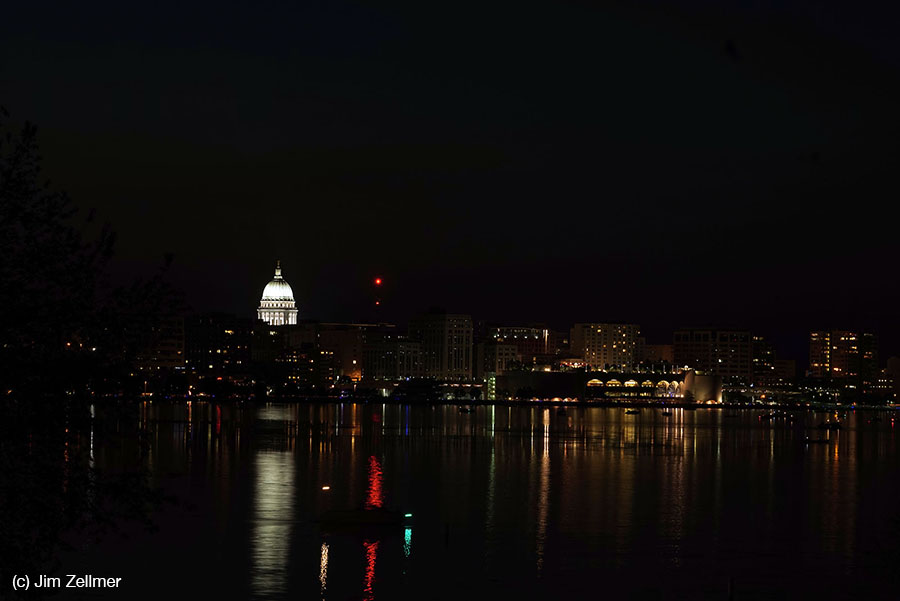
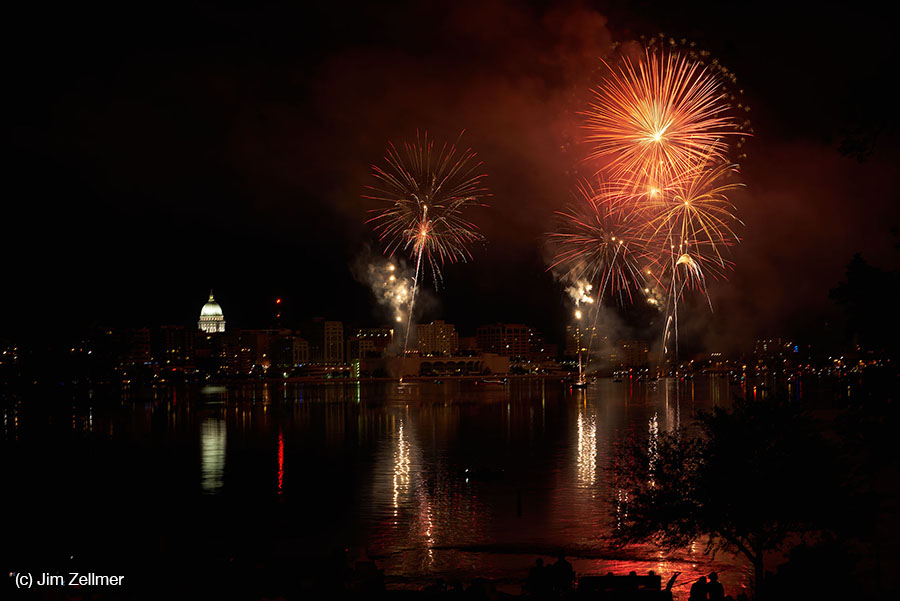
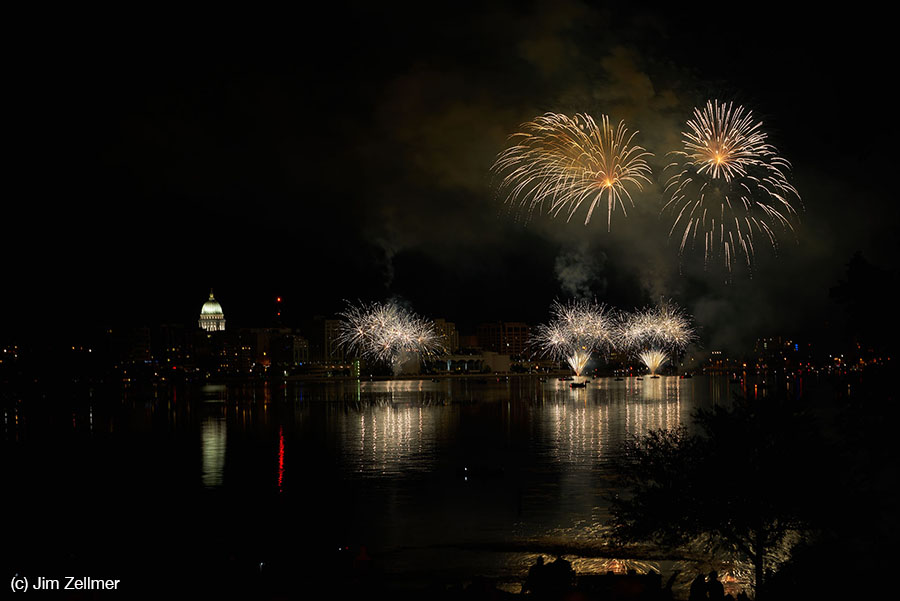
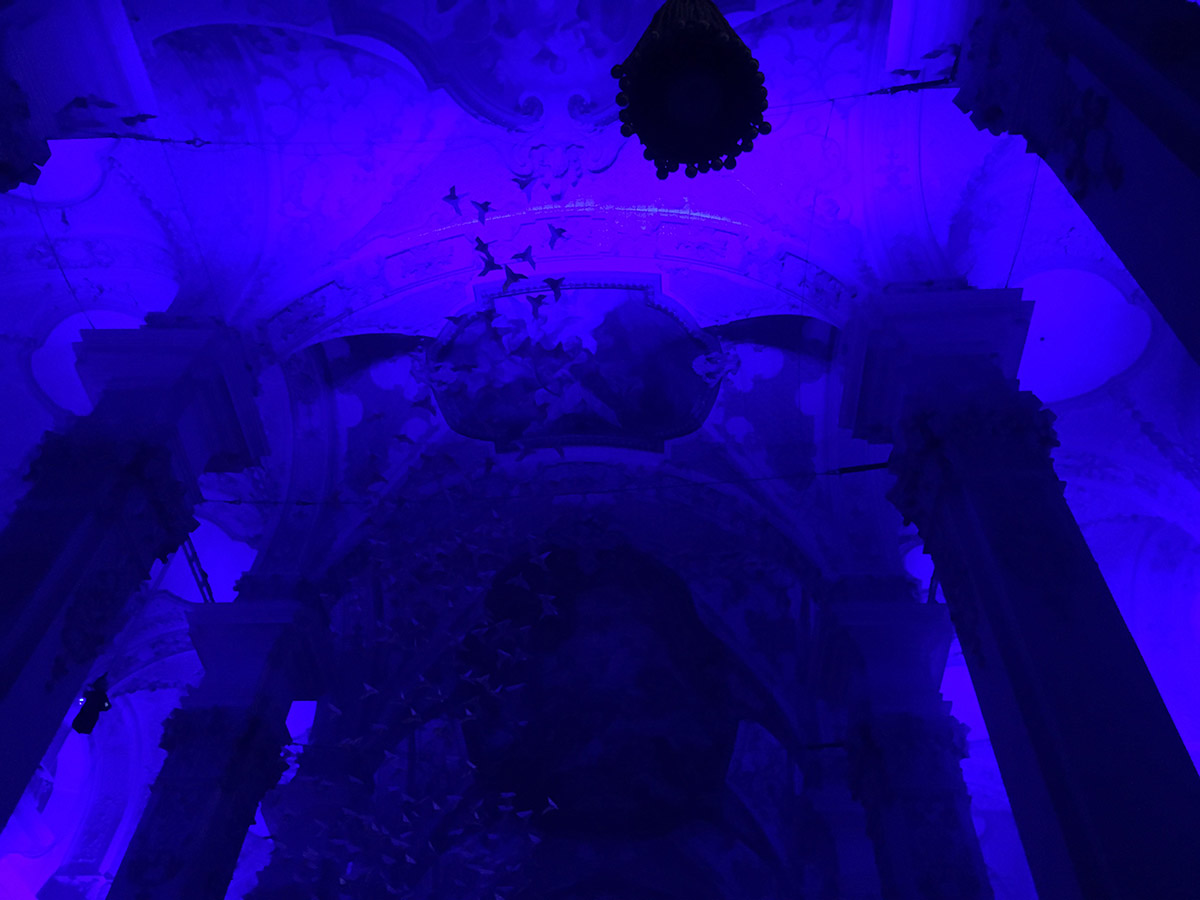
The iPhone has inexorably displaced many traditional cameras. However, there are a number of use cases where the iPhone requires, perhaps too many compromises or is not yet up to the job. Sports, particularly fast movement [1] is one example, while low light is often another.
A recent random left turn brought me to Michael Pendry’s “Les Colombes“.
Pendry’s immersive Pentecost [2] performance offered a great venue to compare the iPhone 6’s low light capabilities with a tradional, full frame sensor [3] digital camera.
iPhone 6 images:
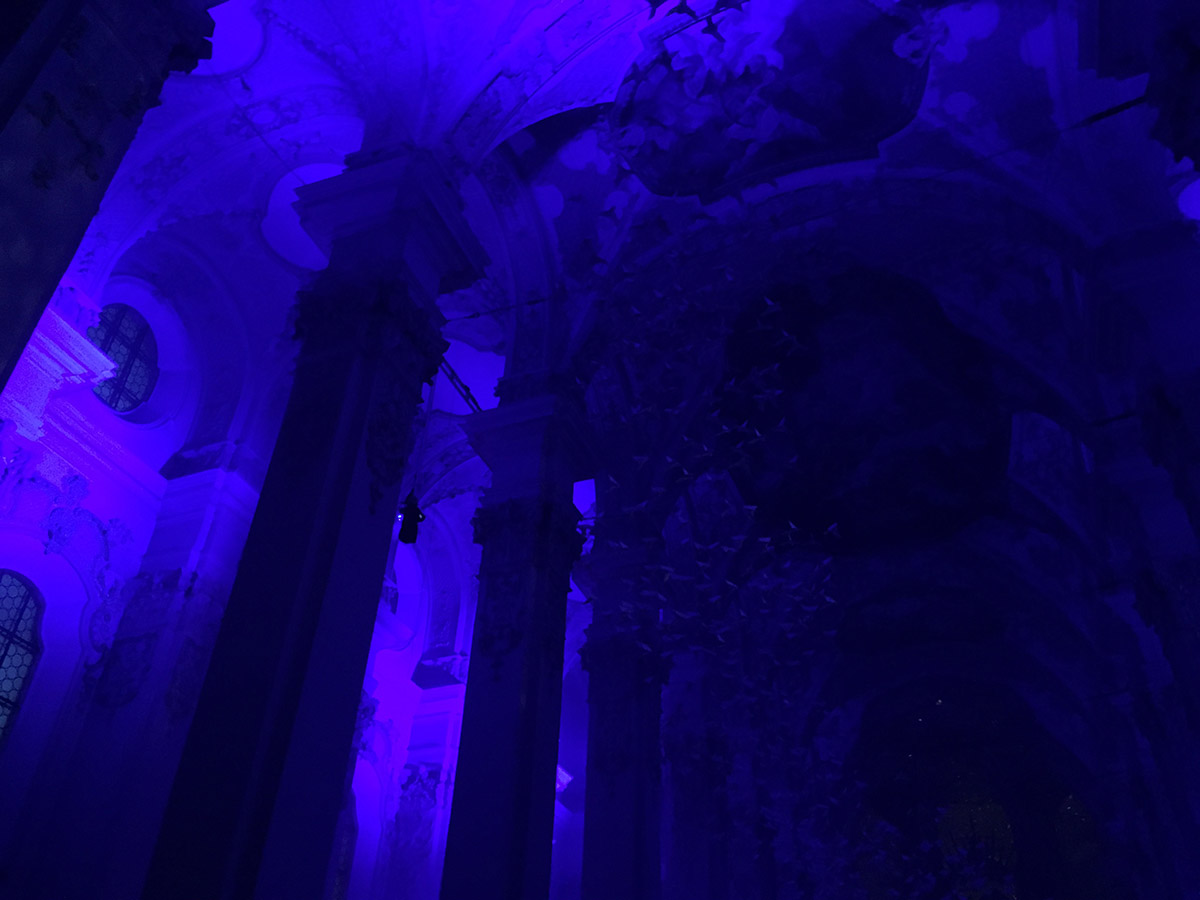
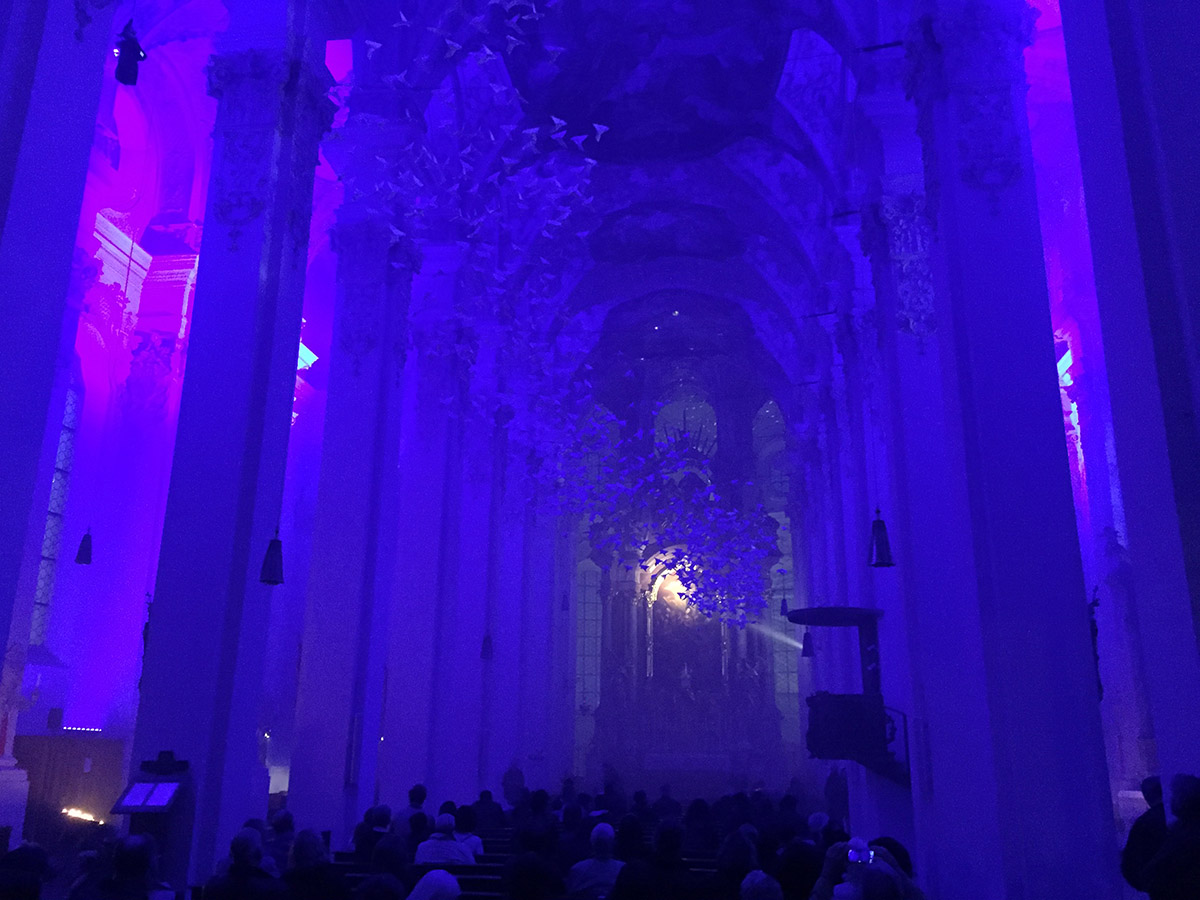




Full frame traditional camera images:
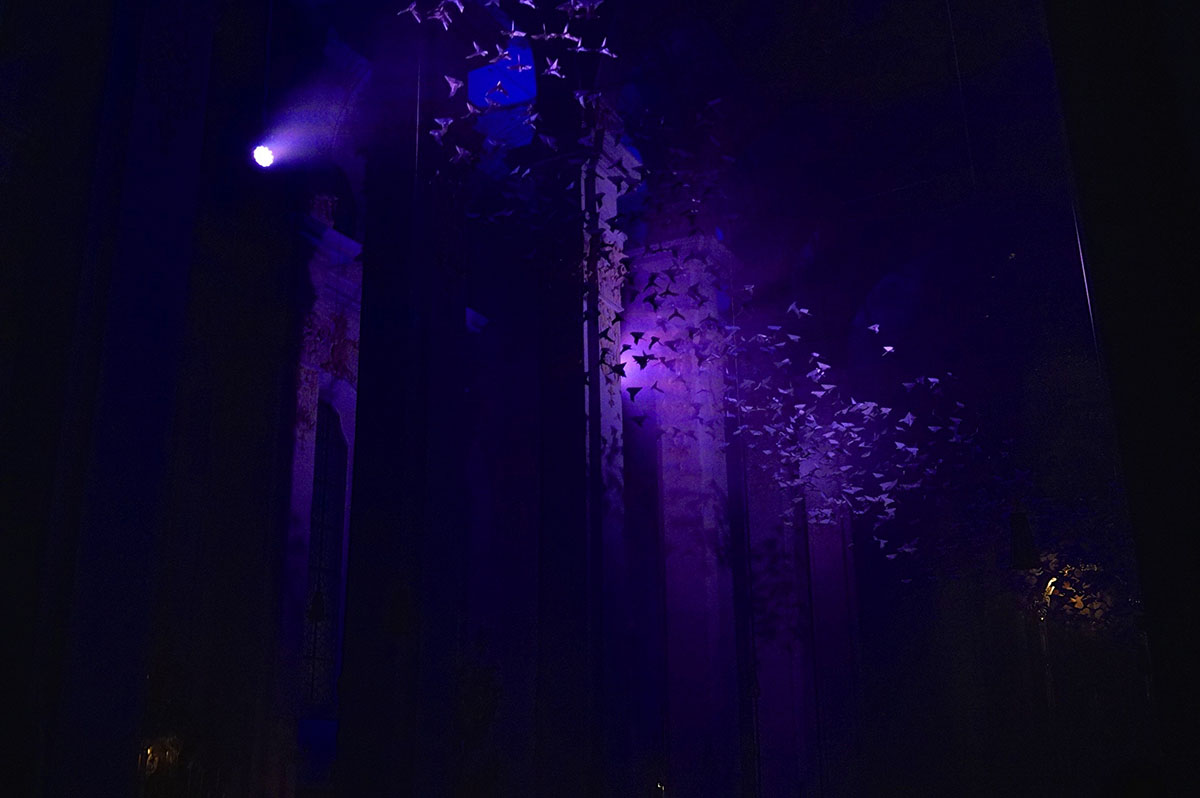
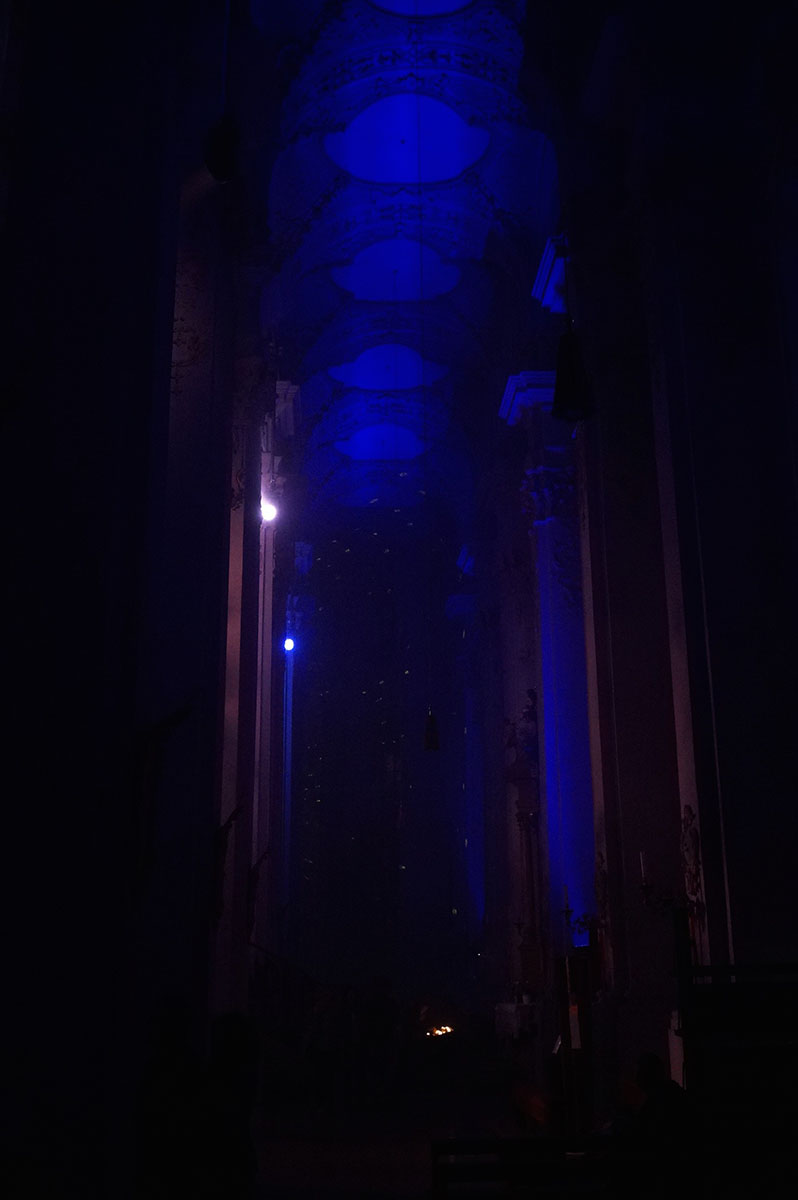
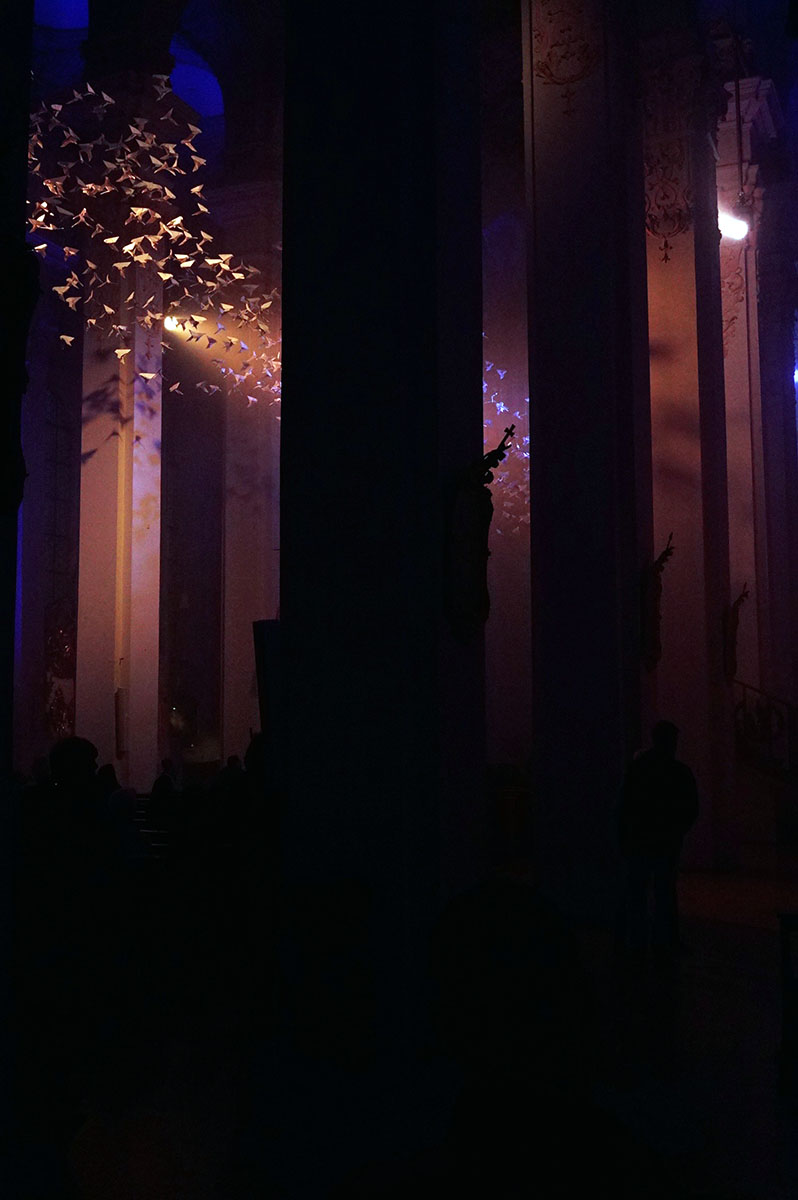
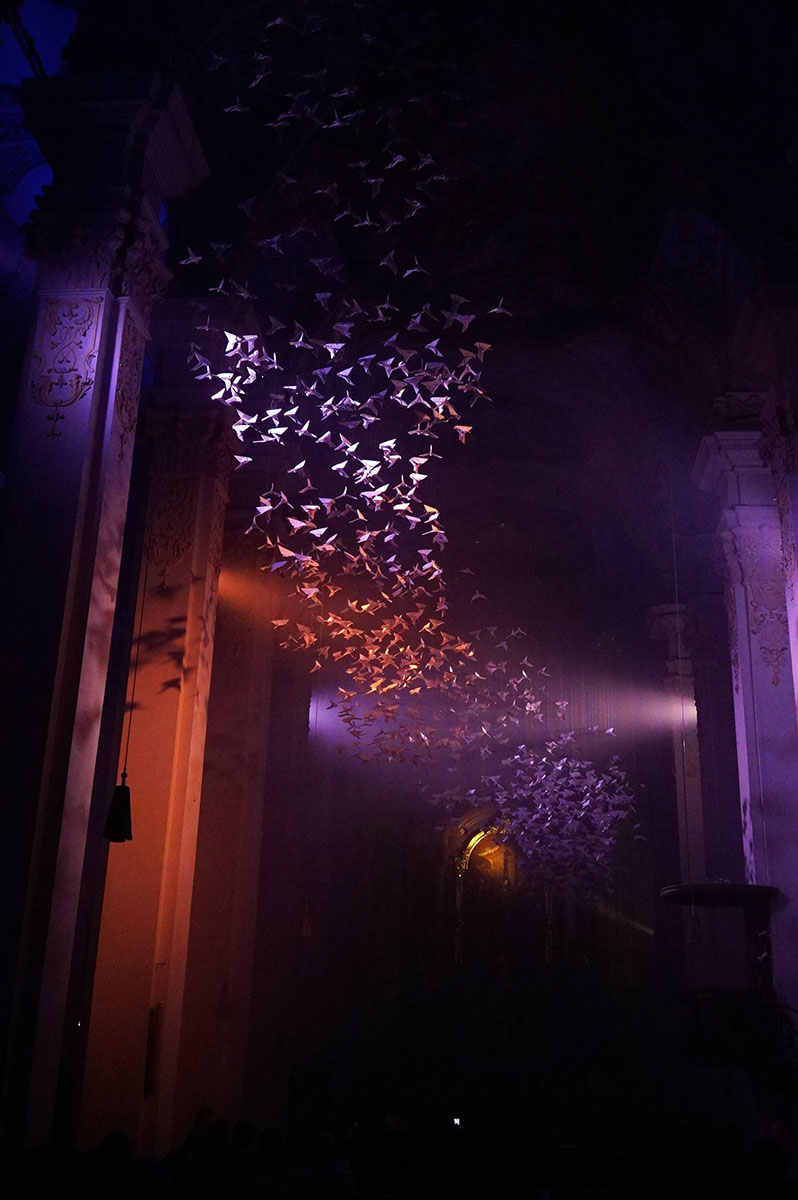





I recorded a short video with this camera as well. Watch it here.
I was pleasantly surprised at the iPhone’s capabilities. While not great compared to the traditional camera, the iPhone performed much better than I expected. Perhaps the next generation or two will require further low light investigation.
View a log of the iPhone’s (growing) photo capabilities, here.
——-
1. iPhone 5s & Sports Photography?.
2. Pentacost.