The Federal Bureau of Investigation, in a review of a national DNA database, has identified nearly 170 profiles that probably contain errors, some the result of handwriting mistakes or interpretation errors by lab technicians, while New York State authorities have turned up mistakes in DNA profiles in New York’s database.
The discoveries, submitted by the New York City medical examiner’s office to a state oversight panel, show that the capacity for human error is ever-present, even when it comes to the analysis of DNA evidence, which can take on an aura of infallibility in court, defense lawyers and scientists said.
The errors identified so far implicate only a tiny fraction of the total DNA profiles in the national database, which holds nearly 13 million profiles, more than 12 million from convicts and suspects, and an additional 527,000 from crime scenes. Still, the disclosure of scores of mistaken DNA profiles at once appears to be unprecedented, scientists said.
Monthly Archives: January 2014
The politics of fear
However, since 9/11 leaders of both political parties in the United States have sought to consolidate power by leaning not just on the danger of a terrorist attack, but on the fact that the possible perpetrators are frightening individuals who are not like us. As President George W. Bush put it before a joint session of Congress in 2001: “They hate our freedoms: our freedom of religion, our freedom of speech, our freedom to vote and assemble and disagree with each other.” Last year President Obama brought the enemy closer to home, arguing in a speech at the National Defense University that “we face a real threat from radicalized individuals here in the United States” — radicalized individuals who were “deranged or alienated individuals - often U.S. citizens or legal residents.”
The Bush fear-peddling is usually considered the more extreme, but is it? The Obama formulation puts the “radicalized individuals” in our midst. They could be American citizens or legal residents. And the subtext is that if we want to catch them we need to start looking within. The other is among us. The pretext for the surveillance state is thus established.
On Bitcoin
A third fascinating use case for Bitcoin is micropayments, or ultrasmall payments. Micropayments have never been feasible, despite 20 years of attempts, because it is not cost effective to run small payments (think $1 and below, down to pennies or fractions of a penny) through the existing credit/debit and banking systems. The fee structure of those systems makes that nonviable.
All of a sudden, with Bitcoin, that’s trivially easy. Bitcoins have the nifty property of infinite divisibility: currently down to eight decimal places after the dot, but more in the future. So you can specify an arbitrarily small amount of money, like a thousandth of a penny, and send it to anyone in the world for free or near-free.
Pomegranates are a Sublime Gift from God

Wikipedia on Pomegranates.
Watch the World Go By: Grand Central Station Panorama

It is always interesting to watch the world go by. Tap or click to step inside the panoramic image, then press and pan in any direction.
Business Partners Fighting Over Fonts
ON DARK evenings in late 1916, a frail 76-year-old man could often be seen shuffling furtively between The Dove, a pub in west London, and the green and gold turrets of Hammersmith Bridge. Passers-by paid no attention, for there was nothing about Thomas Cobden-Sanderson’s nightly walks to suggest that he was undertaking a peculiar and criminal act of destruction.
Between August 1916 and January 1917 Cobden-Sanderson, a printer and bookbinder, dropped more than a tonne of metal printing type from the west side of the bridge. He made around 170 trips in all from his bindery beside the pub, a distance of about half a mile, and always after dusk. At the start he hurled whole pages of type into the river; later he threw it like bird seed from his pockets. Then he found a small wooden box with a sliding lid, for which he made a handle out of tape—perfect for sprinkling the pieces into the water, and not too suspicious to bystanders.
Those tiny metal slugs belonged to a font of type used exclusively by the Doves Press, a printer of fine books that Cobden-Sanderson had co-founded 16 years earlier. The type was not his to destroy, so he concealed his trips from his friends and family and dropped his packages only when passing traffic would drown out the splash. There were slip-ups, all the same. One evening he nearly struck a boatman, whose vessel shot out unexpectedly from under the bridge. Another night he threw two cases of type short of the water. They landed on the pier below, out of reach but in plain sight. After sleepless nights he determined to retrieve them by boat, but they eventually washed away. After that he was more careful.
And, today: Tobias Frere-Jones Is Suing Jonathan Hoefler, via Daring Fireball
RIP: Cash Registers?

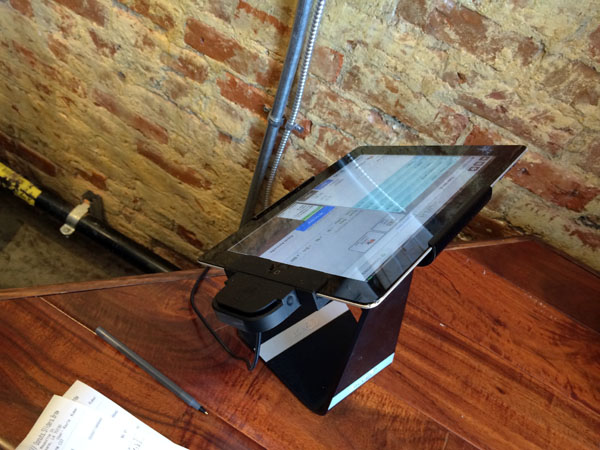
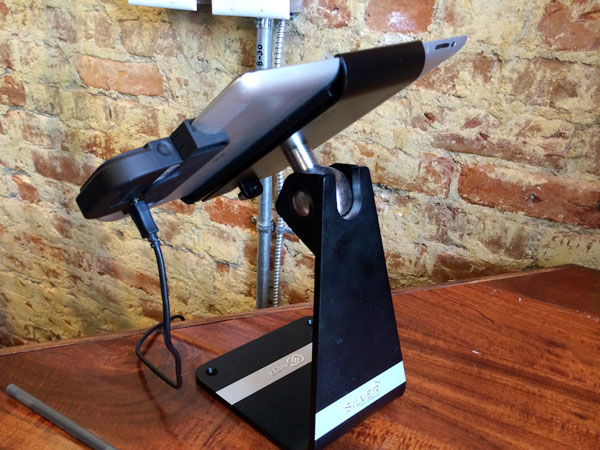
Green Tea. Salad. Oatmeal. Soup. Fruit. Yogurt. Bacon Cheddar Muffin (caught my eye at a sprout style coffee shop, but not for me). These are just a few of the items I’ve purchased when on travel using increasingly popular iPad “cash registers”. Interacting with them more frequently, I’ve begun to catalog installations and reflect on their use.

The term “cash register” [wikipedia] understates much of what the iPad and the supporting cloud software is actually doing. I often ask the attendant or proprietor how they like the iPad + software combination. The most popular response – admittedly, unscientific – is the ease with which they can manage their products and prices. One manager mentioned how difficult it was to reconfigure pricing and products on their previous Windows based “cash register”.

Apps + Cloud
The examples I’ve witnessed use a “cloud” based service: NCR “Silver”, Square and ShopKeep to name a few. The proprietor configures and manages the POS (“Point of Sale”) iPad system from a browser or a management app. Changes are often available immediately. The iPad provides a fast, touch interface to cloud-based data processing. In some ways, this phenomena is a return to the client/server era of the 1990’s.
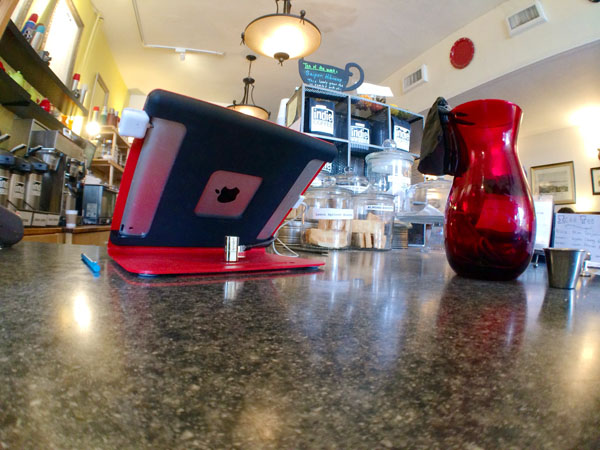

Google Trends “iPad POS”
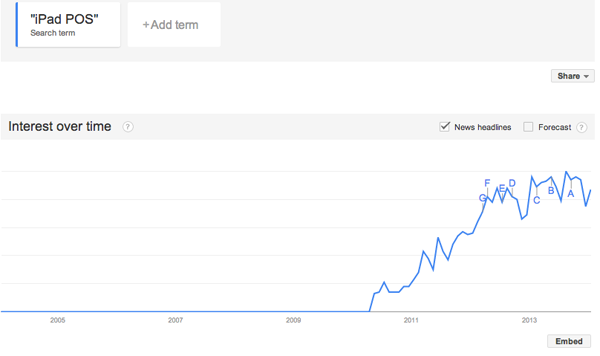
Google Trends “iPad Cash Register”
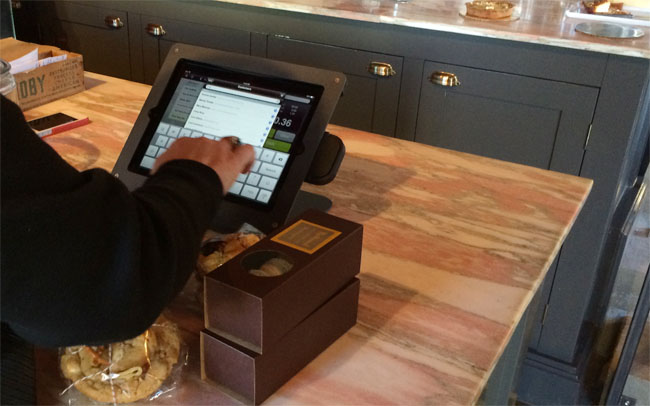
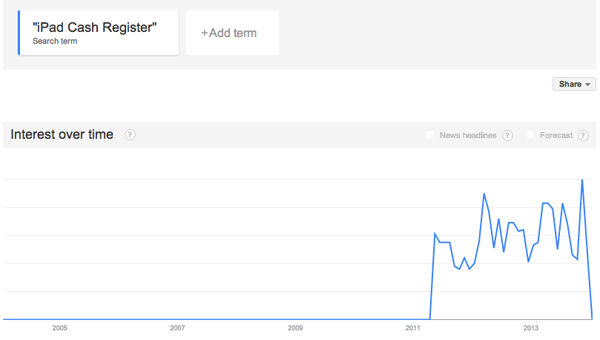

Productivity
I observed a number of clients selecting their contact record to tag a purchase for the store’s affinity program.

This points out another benefit of iPad Point of Sale Apps: clients can often enter or update their own information, saving staff time. The iPad stands quickly rotate so that the customer can complete their information and request a receipt – via email.

I observed one cafe with “black box” 7″ tablets tied to a POS system. Presumably we will see more payment service bundling, particularly from Google, Amazon and others.

But…..
“The cloud is not perfect, it’s not for everyone” – so said the owner of a multi-generation successful restaurant – still using traditional cash registers. I asked this fellow if he considered an iPad cash register app/service?
“You know, the cloud has flaws from privacy to business risk. I’ve looked and looked (and looked) for an iPad POS app that keeps my data local and have yet to find one. I want to control my data.”

Opportunities:
Software
One can imagine many interesting business and service combinations from banking, crm, delivery and ibeacons. New user experiences will emerge, perhaps including “frictionless” purchases via emerging credential services ala Touch ID.
iPad POS system growth is yet another indicator of the iOS eco-system’s strong developer appeal.
Hardware
The next logical step is to eliminate – or make irrelevant – the physical “cash register”, moving the order and payment process to the client’s device such as a smartphone and/or iPad. Perhaps the POS vendors, or one of the eco-system platforms will create and grow a pervasive location aware payment service that interacts with iBeacon-style devices.
Cloud Financial Data
I concur with the proprietor concerned about cloud financial data.
On a related personal data matter, I recently contacted Automatic to see if I might use their auto data tracking device and app without moving all of my information to their services (and “business partners”). I received this response:
This is technically possible, but not as easily done. As long as you have a data plan on your phone, it will upload data to our servers for processing. The only way to prevent it entirely is to not be connected to the internet at all. You’ll still need to connect initially to create an account for the setup process though.
Without an internet connection, trip recording may not work flawlessly all the time as some of it is dependent on our servers for processing. You won’t be able to install any firmware updates for the Link and other features of Automatic won’t work without a connection. Check out this topic in our Community for more information. http://community.automatic.com/automatic/topics/requiring_mobile_data_gps
-Ani
Customer Success
An optimist, I am hopeful that we will see more user controlled data options, soon.
Destiny
I suspect within 5 years (3?) the iPad cash register app model will be old news, largely replaced by location aware client devices.
Notes: The photos above were taken with my iPhone 5s, with the exception of the first, which was taken with my Sigma DP2m. The wood iPad POS stand was my favorite. It was found in a rather high-rent tea cafe.
Detroit motor show: how the US youth fell out of love with car culture The under-35s are driving less and less, a problem that America’s automobile industry is desperate to find a solution to
As the world’s car industry leaders head to the gargantuan Detroit annual motor show this week, many of them will be in the most upbeat mood for years. Sales are back, the car companies are all making profits. But having weathered the worst recession in living memory a big black cloud still hangs above – young people aren’t buying.
Car and youth culture synched gears decisively in 1955. That was when James Dean played chicken in a black Ford Super De Luxe in Rebel Without a Cause. But more recently the love affair between youth and wheels seems to have broken.
New car purchases by those aged 18-34 dropped by 30% in the US between 2007 and 2012, according to the car shopping website Edmunds.com. Many American under-35s are now not even getting their licence. Given that so called “millennials” – those born between 1983 and 2000 – are now the largest generation in the US, the trend is worrying car firms.
Meanwhile the number of miles driven by Americans each year has also started to drop –they now drive fewer miles per capita than at the end of Bill Clinton’s first term, according to a report released last year by US PIRG Education Fund. And the age group showing the biggest decline? Those aged 16 to 34, who drove 23% fewer miles on average in 2009 than in 2001.
Thorium-Fueled Automobile Engine Needs Refueling Once a Century
There are now over one billion cars traveling roads around the world directly and indirectly costing trillions of dollars in material resources, time and noxious emissions. Imagine all these cars running cleanly for 100 years on just 8 grams of fuel each.
Laser Power Systems (LPS) from Connecticut, USA, is developing a new method of automotive propulsion with one of the most dense materials known in nature: thorium. Because thorium is so dense it has the potential to produce tremendous amounts of heat. The company has been experimenting with small bits of thorium, creating a laser that heats water, produces steam and powers a mini turbine.
Current models of the engine weigh 500 pounds, easily fitting into the engine area of a conventionally-designed vehicle. According to CEO Charles Stevens, just one gram of the substance yields more energy than 7,396 gallons (28,000 L) of gasoline and 8 grams would power the typical car for a century.
Stuck: Why Americans Stopped Moving to the Richest States
In 1865, Horace Greeley said “go west, young man,” and, for a century and a half, men and women, young and old, were keen to listen. Even into the early 2000s, the sunbelt stretching into the suburban southwest fattened with new housing developments—ultimately, to disastrous effect. But in the last decade, the ambition to go west has been replaced with a lazier notion—to “stay put.”
“Americans are moving far less often than in the past, and when they do migrate it is typically no longer from places with low wages to places with higher wages,” Tim Noah wrote in Washington Monthly. “Rather, it’s the reverse.” Why America lost her wanderlust is not entirely clear—perhaps dual-earner households make long moves less likely; perhaps the Great Recession pinned underwater homeowners on their plots—but those still wandering aren’t going to the right cities.
When Greeley suggested a westward move, he wasn’t making an argument for sun and gold. He was, above all, suggesting that young people escape from areas with expensive housing: